A
Access Certification: Review and approval of user access rights.Access Control: Restricting access to resources based on user identity.
Access Creep: Accumulation of unnecessary access rights.
Access Management: Process of granting, managing, and revoking access.
Adaptive Authentication: Authentication that adjusts based on context.
API (Application Programming Interface): Set of rules for software interaction.
Application Access: Access granted to specific applications.
Approval Workflow: Automated process for access requests.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Access based on user and resource attributes.
Automated Provisioning: Automatic creation of user accounts.
Automation: Use of technology to streamline processes.
Authorization: Determining what a user is allowed to do.
B
Background Check: Verification of an individual's history.Biometric Authentication: Authentication using biological traits.
Business Process Management (BPM): Managing and optimizing business processes.
Bot: Automated software application.



















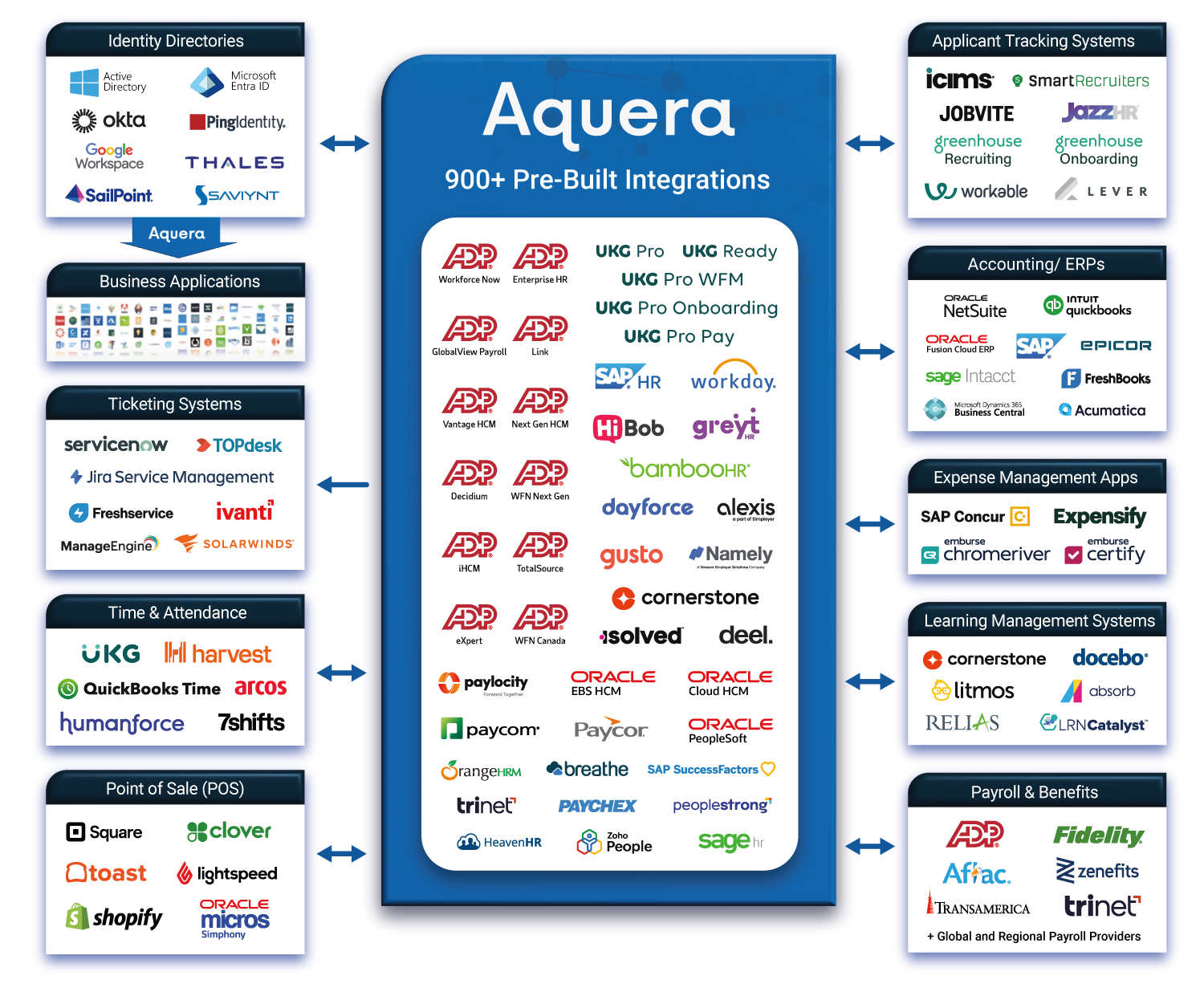
The Aquera 360 HR & Identity Integration as a Service Platform seamlessly integrates any HCM with your organization’s HR, finance, identity directory and IT ecosystems, ensuring automated, end-to-end, employee lifecycle processes, data synchronization, and user account provisioning.
These processes include candidate and employee on/off-boarding, payroll management, and employee access to directories and downstream applications.
Choose from over 900 pre-built connectors for leading business applications including applicant tracking systems, ERPs, third-party HCMs, learning management systems, ticketing systems, payroll services, and identity directories.
C
Cloud Identity: Identity management in a cloud environment.Compliance: Adherence to regulations and policies.
Context-Aware Access: Access based on user context.
Continuous Authentication: Ongoing verification of user identity.
Credential Management: Managing user credentials.
Cybersecurity: Protecting computer systems and networks.
D
Data Governance: Managing the availability, usability, integrity, and security of data.
De-Provisioning: Revoking user access rights.
Delegated Administration: Granting administrative rights to others.
Directory Services: Centralized storage of user information.
Digital Identity: Electronic representation of a person or entity.
Dynamic Authorization: Authorization that changes based on context.
E
Employee Lifecycle Management: Managing all stages of an employee's tenure.
Entitlement Management: Managing user entitlements to resources.
Event-Driven Provisioning: Provisioning triggered by events.
Extensible Markup Language (XML): Data format for information exchange.
F
Federated Identity: Linking identities across different systems.
First-Factor Authentication: Initial authentication method.
H
HR Automation: Automating HR processes.HRIS (Human Resource Information System): Software for managing HR data.
I
IAM (Identity and Access Management): Managing user identities and access.IGA (Identity Governance and Administration): Managing and governing user identities and access.
Identity: Unique attributes that identify a person or entity.
Identity Lifecycle Management: Managing the entire lifecycle of a digital identity.
Identity Provider (IdP): Service that provides authentication.
Information Security: Protecting information assets.
Integration: Connecting different systems together.
IT Governance: Governance of IT resources and processes.
J
Just-in-Time Provisioning: Provisioning user accounts when needed.K
Key Management: Managing cryptographic keys.L
Least Privilege: Granting only necessary access rights.
Lifecycle Management: Managing the stages of a resource or identity.
M
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Using multiple authentication methods.Metadata: Data about data.
O
OAuth (Open Authorization): Authorization framework.Okta: Cloud-based identity management platform.
One-Time Password (OTP): Password valid for a single use.
Orchestration: Automating and coordinating tasks.
P
Password Management: Managing user passwords.Policy Enforcement: Enforcing security policies.
Privileged Access Management (PAM): Managing access to privileged accounts.
Provisioning: Creating and managing user accounts.
R
RBAC (Role-Based Access Control): Access based on user roles.Reconciliation: Comparing user access rights with defined policies.
Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with legal regulations.
Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks.
Role Mining: Discovering and defining user roles.
Role Modeling: Defining roles based on business needs.
Resource Access: Access granted to specific resources.
Review and Certification: Process of reviewing and certifying user access.
S
SaaS (Software as a Service): Software delivered over the internet.SailPoint: Identity governance platform.
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language): XML-based framework for authentication.
Saviynt: Identity governance platform.
SCIM (System for Cross-domain Identity Management): Standard for automating user provisioning.
Second-Factor Authentication: Additional authentication method.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Security monitoring and analysis.
Single Sign-On (SSO): Accessing multiple applications with one set of credentials.
Smart Card: Physical card used for authentication.
Social Login: Logging in using social media accounts.
SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act): US law related to financial reporting.
T
Threat Detection: Identifying potential security threats.Tokenization: Replacing sensitive data with tokens.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Using two authentication factors.
U
User Access Review: Reviewing user access rights.User Account: Record of a user in a system.
User Lifecycle Management: Managing the lifecycle of a user account.
V
Virtual Directory: Directory service that aggregates data from multiple sources.W
Workflow Automation: Automating business workflows.
